


Substation Automation
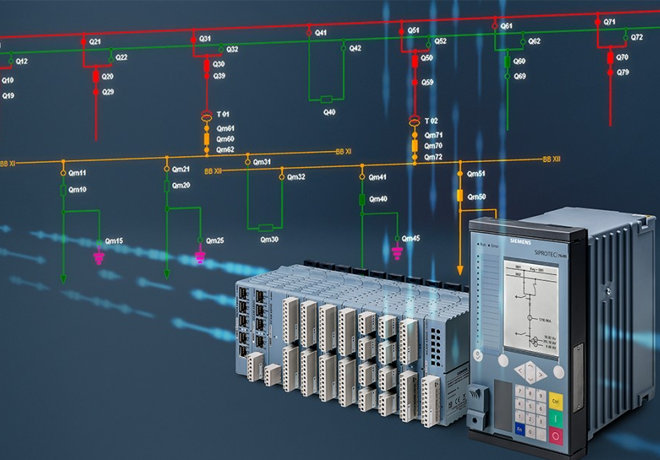
ControlTech provide the integration of advanced technology and control systems into electrical substations, which are critical components of power distribution and transmission networks. We are always keen to achieve objective of substation automation which is to enhance the monitoring, control, protection, and management of electrical substations, ultimately improving the reliability, efficiency, and safety of the power grid. ControlTech serve key components and aspects of substation automation
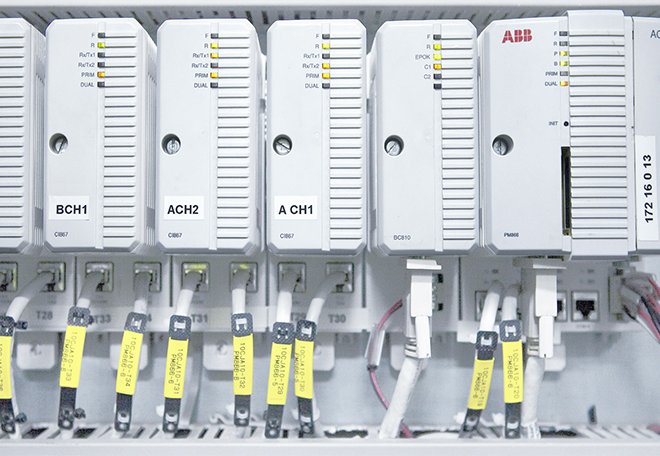
Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs)
These are specialized devices installed in substations to collect data, monitor equipment, and perform control functions. Examples include protective relays, digital meters, and circuit breakers with built-in intelligence. IEDs provide real-time information about the substation’s condition and can take actions to protect the grid when necessary.
Communication Infrastructure
Substation automation relies on robust communication networks to transmit data between devices within the substation and to a central control center. Communication protocols such as IEC 61850, DNP3, and Modbus are commonly used to enable seamless data exchange.
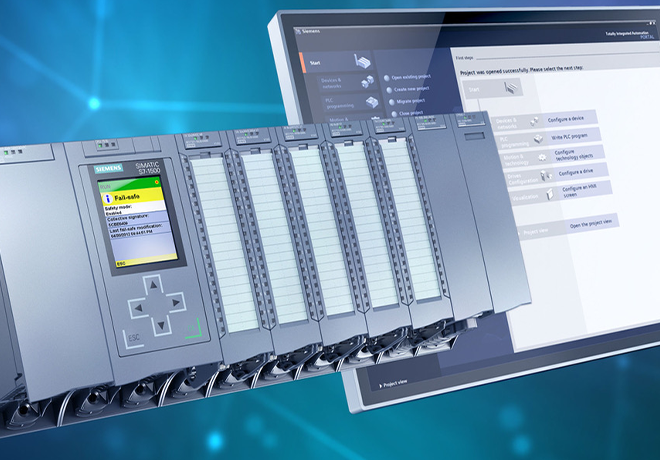
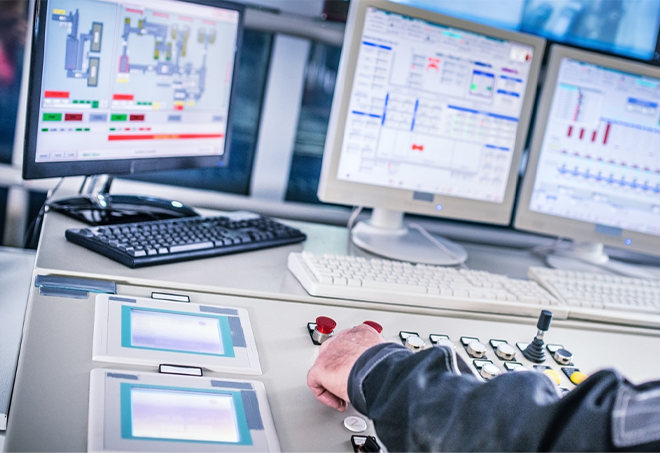
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)
SCADA systems are the core of substation automation. They collect and display real-time data from IEDs, enabling operators to monitor equipment status, voltage levels, current flows, and more. SCADA systems also provide control capabilities, allowing operators to remotely operate circuit breakers, switches, and other devices.
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
RTUs serve as the interface between field devices and the SCADA system. They collect data from IEDs and sensors and transmit it to the central control center. RTUs can also execute control commands from the SCADA system, making them crucial for remote operation and monitoring.
Data Historians and Databases
Substation automation systems store historical data for analysis and reporting. This data helps utilities track equipment performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions about maintenance and upgrades.
Intelligent Control Algorithms
Substation automation systems often incorporate intelligent control algorithms to optimize the operation of the substation. These algorithms can adjust settings, such as voltage regulation and load balancing, to improve grid efficiency.
Cybersecurity Measures
With the increasing connectivity of substation automation systems, cybersecurity is a critical consideration. Robust security measures are implemented to protect against cyber threats and ensure the integrity of data and control functions.
Fault Detection and Protection
Substation automation systems include protective relays that detect and respond to faults and abnormalities in the grid. These relays can trigger circuit breakers to isolate faulty sections and minimize the impact of disturbances.
Remote Diagnostics and Maintenance
Substation automation allows for remote diagnostics of equipment health and performance. This reduces the need for physical inspections and enables proactive maintenance, leading to increased reliability and reduced downtime.
Integration with Grid Management
Substation automation is part of a larger smart grid ecosystem. It integrates with grid management systems, allowing utilities to optimize energy generation, distribution, and consumption in real-time.
Energy Management and Grid Optimization
Substation automation contributes to grid optimization by enabling demand response, renewable energy integration, and load forecasting. This helps utilities manage the grid more efficiently and reduce energy waste.